Theme: “Challenges and Innovations in Nanomedicine and Drug Delivery Researchâ€
NanoDelivery 2018
2nd,International Conference and Exhibition on Nanomedicine and Drug Delivery May 21-23, 2018 Tokyo, Japan
ConferenceSeries Ltd is a renowned organization that organizes highly notable Pharmaceutical Conferences throughout the globe. Currently we are bringing forth “2nd International Conference on Nanomedicine and Drug Delivery” (NanoDelivery 2018) scheduled to be held during May 21-23, 2018 at Tokyo, Japan. The conference invites all the participants across the globe to attend and share their insights and convey recent developments in the field of Nanomedicine and Drug Delivery.
ConferenceSeries Ltd organizes a conference series of 1000+ Global Events inclusive of 1000+ Conferences, 500+ Upcoming and Previous Symposiums and Workshops in USA, Europe & Asia with support from 1000 more scientific societies and publishes 700+ Open access Journals which contains over 50000 eminent personalities, reputed scientists as editorial board members.
2018 Highlights:
- 300+ Participation (70 Industry: 30 Academia)
- 10+ Keynote Speakers
- 50+ Plenary Speakers
- 20+ Exhibitors
- 14 Innovative Educational Sessions
- 5+ Workshops
- B2B Meetings
Nanomedicine and drugdelivery will account for 40% of a $136 billion nanotechnology-enabled drug delivery market by 2021. We forecast the total market size in 2021 to be US$136 billion, with a 60/40 split between nano medicine and drug delivery respectively, although developing new targeted delivery mechanisms may allow more value to be created for companies and entrepreneurs.
However, the Asia-Pacific region is expected to grow at a faster CAGR owing to presence of high unmet healthcare needs, research collaborations and increase in nanomedicine research funding in emerging economies such as Japan, China, India and other economies in the region. Japan is expected to surpass the United States in terms of nanotechnology funding in the near future, which indicates the growth offered by this region.This conference seeks to showcase work in the area of Nanomedicine, Drug Delivery Systems, and nanotechnology, Nanobiothechnology, particularly related to drug delivery.
For More PS: https://nanomedicine.pharmaceuticalconferences.com/
Nanomedicine and drugdelivery can address one of the greatest challenges in the post-genomic era of the 21st century – making the essential connections between Academics and industry professionals.
To meet these challenges, the field of Nanomedicine and drugdelivery has undergone exponential growth during the last 5 years. Technologies such as Personalized Nanomedicine, Design of Nanodrugs, Synthesis of Nanoparticles for Drug Delivery, Regenerative Medicine and Tissue Engineering, Nanomedicines and Biomedical applications, Nanomaterials for drug delivery, Regulatory Aspects Towards Approval of Nanomedicine, NanoPharmaceutical, Industry and Market processing and drug delivery promise to transform the world of Advanced nanomedicines and drug delivery much in the same way that integrated and transformed the world of pharmaceutical sciences.
Nanodelivery 2018 has everything you need:
Open panel discussions: Providing an open forum with experts from academia and business to discuss on current challenges in nanomedicine and drug delivery, where all attendees can interact with the panel followed by a Q&A session.
Speaker and poster presentations: Providing a platform to all academicians and industry professionals to share their research thoughts and findings through a speech or a poster presentation.
Editorial board meeting: Discussing on growth and development of open access Nanomedicine and drugdelivery International Journals and recruiting board members and reviewers who can support the journal.
Round table meetings: Providing a platform where industry professionals meet academic experts.
Over 50+ organizations and international pavilions will be exhibiting at the Nanodelivery 2018 conference and Exhibition. Exhibitors will include equipment manufacturers and suppliers, systems providers, finance and investment firms, R&D companies, project developers, trade associations, and government agencies.
In addition to the products and services you will see at the Nanodelivery Exhibition, you will have access to valuable content, including Keynote Presentations, Product Demonstrations and Educational Sessions from today’s industry leaders.
The Nanodelivery 2018 has everything you need, all under one roof, saving you both time and money. It is the event you cannot afford to miss!
Who's Coming to Nanodelivery 2018?
- CEOs / CMOs
- CTOs
- VPS, Directors, & Managers
- World top Ranked Scientists
- Researchers
- Universities
- Medical Devices
- Pharmaceuticals companies
- Tool and Materials companies And Many More..
Conference Keywords
- Nanomedicine:
- Nanomedicine : Future Nanomedicine:
- Nanomedicine research group:
- Nanomedicine Market:
- Nanomedicine in Cancer:
- New formulations:
- Emergence of Nanomedicines:
- VLPs:
- Nanocarrier:
- Nanomedicine-History:
- Biomedical nanotechnology:
- Drug delivery systems:
- Toxicity:
- Xenobiotics:
- Pharmaceutical technology:
- Bioimaging:
- Imaging probe:
- Pharmaceutical compound:
- Pulmonary delivery:
- Vascular disease:
- Regenerative medicine- self healing:
- Quantitative Imaging:
- Tissue Sciences:
- Rational drug design:
- Drug target:
- Drug resistance mechanism:
- Single molecule imaging:
- Medicine:
- Computer-Aided Diagnosis:
- Pharmacology:
- Drug delivery industries:
- Drug delivery market:
- Nanomedicine Market Size:
- Biodegradable implants:
- Nanomedicine industry:
- Nanomedicine Market Drivers:
- Nanomedicine Market Forecast:
- FDA approved nanomedicine:
Nanomedicine is the medical application of nanotechnology, nanomedicine ranges from the medical applications of nanomaterials and biological devices, to nanoelectronic biosensors, and even possible future applications of molecular nanotechnology such as biological machines.
Nanomedicine : Future Nanomedicine:
We can say that nanomedicine is our future medicine.The usage of Nanomedicine in drug delivery can unlock the way to cure many life threatening diseases. For examples nanomedicine in cancer treatment, Nanomedicine for blood disorders ,Nanomedicine for Lung Diseases , Nanomedicine for Cardiovascular Diseases. This includes Future aspects of Nanomedicine, nanobots, nanodrugs.
This is only possible by the grace and smart work of the nanomedicine research group from all over the world. Nanomedicine courses are taught in the universities all over the world.They also provide postdoctoral fellowship opportunity in nanomedicine .So we can say that future of nanomedicine shines brightly .
Nanomedicine can be explained as the application of nanotechnology to achieve innovation in healthcare.The global nanomedicine market is anticipated to reach USD 350.8 billion by 2025.This includes: Scope of Nanomedicine , Novel Drugs to Nano Drugs, Nanodrugs for Herbal medicines and Cosmetics
A wide range of new tools and possibilities is already achieved in cancer treatments using Nanotechnology, from diagnosing it earlier to improved imaging for targeted therapies.This includes Nanomedicine for other disease, Nanomedicine for Cardiovascular Diseases, Nanodrugs for Cancer Therapy
Nanomedicines are three-dimensional constructs of multiple components with preferred spatial arrangements for their functions.This includes Nano Sized Drugs, Nanodrugs for Veterinary Therapeutics, Nanodrugs for Medical applications, Formulation and Development.
Extensive multidisciplinary investigation in the field of nanomedicine nanotechnology biology and medicine has caused the emergence of Nanomedicine as promising carriers for delivery of diverse therapeutic molecules to the targeted sites. This includes Nanodrugs for Cancer Therapy , Nanodrugs for Veterinary Therapeutics, Nanodrugs for Medical applications.
VLPs are a viruses devoid of genetic material and thus they cannot replicate.This includes NanoMedicine in HIV, Drug targeting, Nanomedicine for Cancer.
A nanocarriers are used as a transport module for a drug. Commonly used nanocarriers include micelles, polymers, carbon-based materials, liposomes and many more.This includes nanoparticles, nanobots, nanodrugs.
It was the extensive multidisciplinary investigation in the field of nanomedicine nanotechnology biology and medicine that gave rise to the future medicine i.e. Nanomedicine. We know that nanotechnology is a recent development in scientific research,though the development of its central concepts happened over a longer period of time.This includes Nanomedicine for other disease, Nanodrugs for Herbal medicines and Cosmetics
Biomedical nanotechnology includes a diverse collection of disciplines.This includes Carbon Nanotubes, Biosensors and Nanobioelectronics, Nanobiomechanics and Nanomedicine.
Drug delivery is the formulations, technologies, and systems for transporting a pharmaceutical compound inside the body safely to achieve its desired therapeutic effect.This includes Liposomes , Versatile Polymers In Drug Deivery , Drug Development
Toxicity :
Toxicity is the measure to which a particular mixture of substances can damage an organism.This include Gold Nanoparticles, Silver Nanoparticles , Magnetic Nanoparticles .
A xenobiotic is a chemical substances which is not produced naturally or expected to be found within an organism.This includes Nano Micro Particles , Biosensors and Nanobioelectronics , Bio inspired materials and drug delivery
We can detect diseases at much earlier stages using Nano pharmaceuticals.Using nanoparticles we can also design the diagnostic applications conventionally.This includes Nanoliposome, Drug Targeting, Challenges and advances in NanoPharmaceuticals
Bioimaging are methods that non-invasively visualize biological processes in real time.This includes Image-guided drug delivery, Imaging, Optical sensors
Molecular imaging probe is an agent used to visualize, characterize and quantify biological processes in living systems .This includes Optical sensors, Smart Polymer Nanoparticles, Nanomaterials for Imaging
The particular pharmaceutical product to fit the unique need of a patient can be made by Pharmaceutical compounding .This includes Challenges and advances in Nano Pharmaceuticals, Nano Pharmaceuticals from the bench to Scale up
Pulmonary delivery of drug has become an attractive target and of tremendous scientific and biomedical interest in the health care research .This includes Transmucosal Drug Delivery Systems, Sonophoresis Drug Delivery System, Hydrogel in Drug Delivery
Diseases of the blood Vessels can be related to Vascular diseases.This includes ovarian, breast cancer, kidney disease, fungal infections.
The use of a tissue, engineering and materials methods, and suitable biochemical and physicochemical factors to improve or replace biological tissues.This includes Neuro Regenerations, Organ fabrication, Cell-based therapies
Regenerative medicine is a broad field that includes tissue engineering but also incorporates on self-healing
Regenerative medicine- self healing:
Body uses its own systems, sometimes with help foreign biological material to recreate cells and rebuild tissues and organs.This include Biologic scaffolds, Bone Marrow Tissue Engineering , Mechanical properties of engineered tissues
Quantitative imaging provides clinicians with a more accurate picture of a disease state.This includes Image-guided drug delivery, Imaging , Optical sensors .
The internal organs and connective structures of vertebrates, and cambium, xylem, and phloem in plants are made up of different types of tissue.This includes Neuro Regenerations, Bioreactor design, Bone Marrow Tissue Engineering.
Drug design, is simply the inventive process of finding new medications based on the knowledge of a biological targetThis includes Nanodrugs for Cancer Therapy, Nanodrugs for Medical applications, Nano Sized Drugs
Biological target can be described as the native protein in the body , with modified activity by a drug resulting in a specific effect. The biological target is often referred to as a drug target.This include Drug targeting, Image-guided drug delivery , target site
In Drug resistance the effectiveness of a medication is reduced such as an antimicrobial or an antineoplastic in curing a disease or condition.This includes chemotherapy, tumor-targeted drug delivery
Single-molecule studies may be contrasted with measurements on the bulk collection of molecules. In this individual behavior of molecules cannot be distinguished, and only average characteristics can be measured.This include Drug targeting, Image-guided drug delivery, Imaging
Medicine can be explained as the science and practice of the diagnosis, treatment, and prevention of disease .This include Controled radical polymerization, Nanodrugs for Herbal medicines and Cosmetics, Nanomedicine for Gastrointestinal Tract (GI) Diseases.
Computer-aided detection (CADe), are systems that help doctors in the interpretation of medical images.This includes Image-guided drug delivery, Optical sensors, Biosensors and Nanobioelectronics
Pharmacology is the study of drug action, where a drug can be broadly defined as any man-made, natural, or endogenousThis includes Nanoliposome, Drug Targeting, Applied biopharmaceutics
Demand for drug delivery products in the US will rise 6.1 percent yearly to $251 billion in 2019. Parenteral products will grow the fastest, driven by monoclonal antibodies and polymer-encapsulated medicines. Hormones and central nervous system agents will lead gains by application. Pen injectors and retractable prefillable syringes will pace devices.This includes Bio Pharmaceutical Industry, Focus on Nanopharmaceuticals, Industrial Applications of Nano medicine.
The drug delivery market is the largest contributing application segment, whereas biomaterials is the fastest growing application area in this market. Nanomedicine accounts for 77 Marketed Products Worldwide, representing an Industry with an estimated market $130.9 Billion by 2016.This includes Bio Pharmaceutical Industry, Focus on Nanopharmaceuticals, Industrial Applications of Nano medicine.
The global nanomedicine market is anticipated to reach USD 350.8 billion by 2025, according to a new report by Grand View Research, Inc. Development of novel nanotechnology-based drugs and therapies is driven by the need to develop therapies that have fewer side effects and that are more cost-effective than traditional therapies, in particular for cancer.This includes pharmaceutical industry, Up Coming Market for Nanotechnology, Focus on Nanopharmaceuticals.
Biodegradable implants offer a number of financial, psychological, and clinical advantages over permanent metal implants.They provide the appropriate amount of mechanical strength when necessary, and degrade at a rate similar to new tissue formation, thereby transferring the load safely to the healed bone and eliminating the need for an additional revision and removal operation.This includes Biologic scaffolds, Biomaterials, Bone Marrow Tissue Engineering.
Expected developments in nanorobotics owing to the rise in funding from the government organizations is expected to induce potential to the market. Nanorobotics engineering projects that are attempting to target the cancer cells without affecting the surrounding tissues is anticipated to drive progress through to 2025.This includes Industrial Applications of Nano medicine, Nanotechnology tools in Pharmaceutical R&D, Bio Pharmaceutical Industry, Focus on Nanopharmaceuticals
The major drivers of the nanomedicine market include its application in various therapeutic areas, increasing R&D studies about nanorobots in this segment, and significant investments in clinical trials by the government as well as private sector. The Oncology segment is the major therapeutic area for nanomedicine application, which comprised more than 35% of the total market share in 2016.This includes An Up and Coming Market for Nanotechnology, Nanomedicine: Prospects, Risks and Regulatory Issues, Current , Future Applications and Regulatory challenges.
The therapeutic areas for nanomedicine application are Oncology,is includes Current , Future Applications and Regulatory challenges, Regulatory Policies.
When the report provides complete details about the usage and adoption rate of nanomedicines in various therapeutic verticals and regions. With that, key stakeholders can know about the major trends, drivers, investments, vertical player’s initiatives, government initiatives towards the nanomedicine adoption in the upcoming years along with the details of commercial drugs available in the market.This includes Regulation of Nanomedicines, Nanomedicine: Prospects, Risks and Regulatory Issues, Current , Future Applications and Regulatory challenges.
Focusing on critical issues relevant to nanoproduct development and translational activities, it tackles topics such as regulatory science, patent law, FDA law, ethics, personalized medicine, risk analysis, toxicology, nano-characterization and commercialization activities.This includes Industrial Applications of Nano medicine, Nanotechnology tools in Pharmaceutical R&D, Bio Pharmaceutical Industry.
The field of Nano Delivery now has pivotal roles in electronics, biology and medicine. Its application can be appraised, as it involves the materials to be designed at atomic and molecular level. Due to the advantage of their size, nanospheres have been shown to be robust drug delivery systems and may be useful for encapsulating drugs and enabling more precise targeting with a controlled release. In this review specifically, we highlight the recent advances of this technology for medicine and drug delivery systems. Nanomaterials range from 10–200 nm up to a few micrometres in size, and include nano- and microparticles, nanotubes and quantum dots.
Nanotechnological devices are made from metals, polymers, lipids and organic substances as well as from macromolecules such as dendrimers, antibodies, micelles, liposomes and nanofibers. Nanomedicine makes use of these nanostructures for diagnostic or therapeutic applications in all fields of medicine, using them for drug delivery, biosensors, neuro-electronic interfaces, in vivo imaging, and cell-specific molecular interactions, where "cell repair machines" could revolutionize medicine and the medical field. As drug delivery systems, nanoparticles can be designed to improve the pharmacological and therapeutic properties of drugs. The strength of nanoparticulate drug delivery systems is their ability to alter the pharmacokinetics and biodistribution of drugs.
ConferenceSeries Ltd organizes a conference series of 3000+ Global Events with over 600+ Conferences, 1200+ Symposiums and 1200+ Workshops in USA, Europe & Asia with support from 1000 more scientific societies and publishes 700+ Open access journals which contains over 30000 eminent personalities, reputed scientists as editorial board members.
Track 1: Advanced Nanomedicine
Advanced Nanomedicine seeks to deliver a valuable set of research tools and clinically useful devices. The pharmaceutical industry is developing new commercial applications that may include advanced drug delivery systems, new therapies, and Nanomaterials for Imaging and Drug Delivery. Another active and very much related area of research is the investigation of toxicity and environmental impact of nanoscale materials, since nanomedicines must be biocompatible for clinical application.
Track 2: Design of Nanodrugs
To reach target cell, designing of nanodrugs are major aspects, where researcher interested for developing novel Nanodrugs.
Aimed and specially designed session for researchers developing Nanodrugs for delivery of amino acids, Nucleic acids and proteins. The session Design of Nanodrugs includes: Novel Drugs to Nano Drugs, Nanodrugs for Cancer Therapy, Nanodrugs for Veterinary Therapeutics, Nanodrugs for Medical applications and Nanodrugs for Herbal medicines and Cosmetics.
Track 3: Nanomedicine and Nanotechnology
Nanotechnology for cancer is a field that incorporates the studies related to nanosized particles, their function and behavior with respect to different systems. The tremendous capabilities of nanoparticles have changed the perspective and scope of nanotechnology towards development into an adjuvant field for the remaining fields of life sciences. The role of nanotechnology in the field of pharmaceutics has tremendously changed the way of our understanding about drugs, nanodrugs or the use of nanoparticles as carrier of drug has become the basic fundamental or criteria for the production or design of a drug and advances in nanotechnology.
Nanotechnology is an important field of modern research dealing with design, synthesis, and manipulation of particle structures ranging from approximately 1-100 nm.
The session Design of Nanomedicine and Nanotechnology includes broad topics like: Carbon Nanotubes, Nanoparticles, Gold Nanoparticles, Silver Nanoparticles, Magnetic Nanoparticles, Nano Micro Particles, Nanocomposite Microspheres, Biosensors and Nanobioelectronics, Bio inspired materials and drug delivery and Nanobiomechanics and Nanomedicine.
Track 4: Synthesis of Nanoparticles for Drug Delivery
Nanoparticles (NPs) have wide range of applications in areas such as health care, cosmetics, food and feed, environmental health, mechanics, optics, biomedical sciences, chemical industries, electronics, space industries, drug-gene delivery, energy science, optoelectronics, catalysis, single electron transistors, light emitters, nonlinear optical devices, and photo-electrochemical applications.
Synthesizing nanoparticles for pharmaceutical purposes such as drug preparation can be done in two methods. Bottom up process such as pyrolysis, inert gas condensation, solvothermal reaction, sol-gel fabrication and structured media in which hydrophobic compound such as liposomes are used as bases to mount the drug. Top down process such as attrition / milling in which the drug is chiseled down to form a nanoparticle
Nanocarriers, Gold Nanoparticles, Silver Nanoparticles, Liposomes, ligands, Nanoemulsions , Solid Lipid Nanoparticles, Polymeric Nanoparticles, Dendrimer Nanocarriers, Silica materials and Carbon Nanocarriers, nanotechnology and medicine.
Track 5: Regenerative Medicine and Tissue Engineering
The promise of regenerative medicine is truly remarkable. Regenerative medicine is a new branch of medicine that attempts to change the course of chronic disease, in many instances regenerating failing organ systems lost due to age, disease, damage, or congenital defects. The area is rapidly becoming one of the most promising treatment options for patients suffering from tissue failure.
Tissue Engineering and Regenerative Medicine is appealing to scientists, physicians, and lay people alike: to heal tissue or organ defects that the current medical practice deems difficult or impossible to cure.
It covers numerous topics, such as stem cells, cell culture, polymer synthesis, novel biomaterials, drug delivery, therapeutics, and the creation of tissues and organs.
This session dedicated to helping provide research-based solutions to issues related to human diseases and include with sessions as: tissue engineering, Organ fabrication, Tissue printing, Biomaterials, Biologic scaffolds, Hydrogels, Cell seeded matrices, Bioreactor design, Mechanical conditioning of engineered tissues, Mechanical properties of engineered tissues, Physiological properties of engineered tissues, Clinical outcomes of engineered tissue implantation, Cell-based therapies.
Track 6: Nanomedicine in Theranostics
Theranostic nanomedicine is emerging as a promising therapeutic paradigm. It takes advantage of the high capacity of nanoplatforms to ferry cargo and loads onto them both imaging and therapeutic functions. The resulting nanosystems, capable of diagnosis, drug delivery and monitoring of therapeutic response, are expected to play a significant role in the dawning era of personalized medicine, and much research effort has been devoted toward that goal.
Track 7: Nanomedicines and Biomedical Applications
Nanomedicine seeks to deliver a valuable set of research tools and clinically useful devices. The pharmaceutical industry is developing new commercial applications that may include advanced drug delivery systems, new therapies, and Nanomaterials for Imaging and Drug Delivery. Another active and very much related area of research is the investigation of toxicity and environmental impact of nanoscale materials, since nanomedicines must be biocompatible for clinical application.
Track 8: Drug Delivery Research
Drug Delivery Conferences attains greater global significance as Drug Delivery plays a significant role in the future of pharmaceutical research Novel drug delivery system method by which a drug is delivered can have a significant effect on its efficacy. Conference includes topics like lipid Polymers to enhance drug delivery technology by providing controlled release of therapeutic agents in constant doses over long periods, cyclic dosage, and tunable release of both hydrophilic and hydrophobic drugs. In vitro & in vivo dissolution testing is required to ensure that drug dissolves at a consistent rate from batch to batch of formulated drug product. Improvement of dissolution rate of poorly soluble drugs can be increased by dissolving them in liquid hydrophilic vehicles followed by soaking on highly porous materials. The major part is to deliver an innovative speech on the latest Targeted drug delivery is a method of delivering medication to a patient in a manner that increases the concentration of the medication in some parts of the body relative to others. Pharmacokinetic behavior in drug design and drug development for safety issues arising either as a result of animal toxicity testing or in the clinical program itself
Track 9: Novel Drug Delivery Systems
To maximize knowledge of the current researcher on developing drug delivery systems via Novel techniques for Pharmaceutical formulation development, Drug Delivery conference themed quality topics on Liposomes, Dendrimer, Targeted Drug Delivery design, versatile polymer in Drug Delivery and Controlled Drug Delivery, Trans mucosal Drug Delivery, Blood Brain Barrier, Optimization of pharmaceutical products, Sustained Drug Delivery Systems, are a uniquely architect session to play an important role in the fields of pharmaceutical formulation development and Pharmacology.
Track 10: Smart Drug Delivery Technology
To maximize knowledge of the current researcher on developing drug delivery via Pharmaceutical formulation, Smart Drug Delivery conference themed quality topics on Drug Targeting, Drug Designing, Drug evaluation, Drug Delivery and Therapeutics, Biodegradable polymers, Dendrimer a versatile polymer in drug delivery are a uniquely architect session to play an important role in the fields of nanotechnology, pharmaceutical and medicinal chemistry.
Major drugs driving growth of the overall smart drug delivery market include Angiomax, Copaxone, Forteo, Sandostatin, Velcade, Victoza and Zoladex
Track 11: Nano Pharmaceuticals
Pharmaceutical Nanotechnology for Drug Delivery using Nanotechnology session plays major role in the future of pharmaceutical research. In this session, we will go over several of the most important features of nanotechnology, anticancer drug development , pharmocology of cancer drugs, that will impact our lives but we will also talk about what nanotechnology itself will be like in the future and Investigator specifically from cancer therapy. Interestingly pharmaceutical sciences are using nanoparticles to reduce toxicity and side effects of drugs and up to recently did not realize that carrier systems themselves may impose risks to the patient.
Nano technology session includes drug delivery using nanotechnology, Pharmaceutical technology, Nanoparticles permeability to BBB, Cancer drug targets, Nanoparticles application, Pancreatic Cancer, Nanoliposome-mediated delivery, MicroRNA therapeutics, recent breakthroughs in nanoparticle design to demonstrate their high potential as multifunctional drug delivery nanocarrier, Carriers for nanotechnology, various nanostructures, magnetic nanoparticles. In this review Polymer Nanotechnology for Drug Delivery, Nano composite materials, to deliver highly efficient therapeutic compounds to patient a future aspect of Nanotechnology has a vast future ahead of it and we are constantly making breakthroughs in this industry every day.
Track 12: Biopharmaceutics and Biologic Drugs
Biopharmaceutics is defined as the study of factors influencing the rate and amount of drug that reaches the systemic circulation and the use of this information to optimise the therapeutic efficacy of the drug products. The process of movement of drug from its site of administration to the systemic circulation is called as absorption. The concentration of drug in plasma and hence the onset of action, and the intensity and duration of response depend upon the bioavailability of drug from its dosage form. Bioavailability is defined as the rate and extent (amount) of drug absorption.Biologic Drugs, or biologic response modifiers, are medications genetically engineered from a living organism, such as a virus, gene or protein, to simulate the body’s natural response to infection and disease. Biologics target proteins, cells and pathways responsible for the symptoms and damage of rheumatoid arthritis and other types of inflammatory arthritis. Biologic response modifiers (biologics for short) are drugs that are genetically engineered from a living organism, such as a virus, gene or protein, to simulate the body’s natural response to infection and disease.
Track 13: Nano Biotechnology
Nanobiotechnology is the intersection of nanotechnology and biology. Nanobiotechnology has multitude of potentials for advancing medical science thereby improving health care practices around the world. Nanomedicine is used to treat diseases by gene therapy. Nano biotechnologies are being applied to molecular diagnostics and several technologies are in development.
Track 14: Nano Pharmaceutical Industry and Market
Nano Pharmaceutical Industry Companies and Market session is beginning to change for small, medium, and large scale pharmaceutical Co, biopharmaceutical Manufacturing and Industries , generic drugs companies, contract drug delivery companies which can manifest from development to manufacturing. Addressing these instabilities is a great challenge, because of the complexity of the Clinical bio therapeutics themselves. This session includes Rheological behavior, Pharmaceutical Guidelines, Pharmaceutical companies and regulatory guidelines perspectives, Advances in computational modeling for bioavailability, drug Stability of Pharmaceutical products which are driving crucial research into new vaccines and medicines. The pharmaceutical industry and the public sector are thinking differently than before about how to improve access to medicines and advance research and development for neglected diseases.
Track 15: Regulatory Aspects Towards Approval of Nanomedicine
Nanoethics is the study ethical and social implications of nanotechnology’s. It is an emerging but controversial field. Nanoethics is a debatable field. As the research is increasing on nanomedicine, there are certain regulations to increase their efficacy and address the associated safety issues. Other issues in nanoethics include areas like research ethics, environment, global equity, economics, politics, national security, education, life extension and space exploration.
Related Conferences:
Nanomaterials Conference March 30- 31, 2017 Madrid,Spain; Medical Nanotechnology Summit May 22-23, 2017 Osaka, Japan; Molecular Nanoscience Meeting October 20-22, 2016 Rome, Italy; Nanotechnology Expo November 10-12 2016, Australia; Nanotech Expo December 5-7 2016, USA; International Conference on Nanoscience and Nanotechnology (ICONN), 7–11 February 2016, Australia; International Conference on Nanobiotechnology, Drug Delivery, and Tissue Engineering, 1st - 2nd April 2016, Czech Republic; International Conference on Biotechnology, Bioengineering and Nanoengineering, April 14-15, 2016, Portugal; Meeting and Expo on Nanomaterials and Nanotechnology, 25th - 27th April 2016, UAE; NANOTEXNOLOGY , 2–9 July, 2016, Greece. Nano Canadian Society, American Nano Society, American Society for Nanomedicine, Society for Personalized Nanomedicine.
Summary of Nanodelivery 2018 Conference:
Nano Delivery 2018 is an emerging field of engineering and life sciences that promises to revolutionize medicine and medical technology. There are numerous applications of nanomedicine and Drug Delivery using Nanotechnology in medicinal diagnostics. These include improved imagining of the human (or any) body and detecting tumors that are only a few cells in size.
The idea that pharmaceutical agents should be delivered specifically to diseased cells holds the promise of a variety of benefits. The promise of individualized medicine is that it is efficient. Targeted drug-delivery allows doctors and patients to benefit from small dosages at just the right place and thus from fewer side effects.
Nanomedicine has therapeutic uses as well. Nanotechnology is capable of delivering medication to the exact location where they are needed, hence lesser side effects. It can also be used to destroy harmful organisms or cancer cells by interrupting their division process. Nanoprobes can be made to generate radiation that could kill bacteria, viruses and cancer cells. Nanotechnology also theoretically allows the mimicking of natural biological processes, e.g. repair of damaged tissues or acting as artificial red blood cells to transport oxygen.
The global market for healthcare nanotechnology is expected to reach USD 196.02 billion by 2020 growing at a CAGR of 12.1%, according to a new study by Grand View Research, Inc. Increasing susceptibility of patients towards chronic diseases such as cardiovascular, neurological, oncology and respiratory diseases coupled with increasing R&D spending opening new application avenues is expected to drive market growth over the next six years. Other drivers of this market include increasing government and private sector R&D aid and new players entering the market to bridge the gap between supply and demand.
Importance & Scope of Nano Delivery:
Researchers are developing a nanoparticle that can be taken orally and pass through the lining of the intestines into the bloodsteam. This should allow drugs that must now be delivered with a shot to be taken in pill form. The researchers have demonstrated the technique with lab mice so far.
Researchers are also developing a nanoparticle to defeat viruses. The nanoparticle does not actually destroy viruses molecules, but delivers an enzyme that prevents the reproduction of viruses molecules in the patients bloodstream. The effectiveness of the technique has been demonstrated in lab tests.
About venue:
Tokyo is Japan's capital and the world's most populous metropolis. It is also one of Japan's 47 prefectures, consisting of 23 central city wards and multiple cities, towns and villages west of the city center. The Izu and Ogasawara Islands are also part of Tokyo. Prior to 1868, Tokyo was known as Edo. A small castle town in the 16th century, Edo became Japan's political center in 1603 when Tokugawa Ieyasu established his feudal government there. A few decades later, Edo had grown into one of the world's most populous cities. With the Meiji Restoration of 1868, the emperor and capital moved from Kyoto to Edo, which was renamed Tokyo ("Eastern Capital"). Large parts of Tokyo were destroyed in the Great Kanto Earthquake of 1923 and in the air raids of 1945.
Today, Tokyo offers a seemingly unlimited choice of shopping, entertainment, culture and dining to its visitors. The city's history can be appreciated in districts such as Asakusa, and in many excellent museums, historic temples and gardens. Contrary to common perception, Tokyo also offers a number of attractive green spaces in the city center and within relatively short train rides at its outskirts.An ancient city that has grown organically rather than according to an imposed plan, Tokyo exhibits a layout that differs radically from the grid-like patterns of cities like Washington, D.C., or Chicago. The streets follow no discernible pattern, though they might approximate a spiderweb, with concentric circles like Meiji-dori intersected by radiating streets like Shinjuku-dori and Yamate-dori. The geographical center is arguably Chiyoda-ku, where the Imperial Palace is located, though Chiyodaku, with its abundant public park space, hardly qualifies as Tokyo's "downtown." No other area qualifies as downtown either; instead, the city has several concentrated "centers," such as Shibuya, Shinjuku, and Ikebukuro. Other hubs include Setagaya, the Ginza, and Ueno.
The Tokyo region is Japan's leading industrial center, with a highly diversified manufacturing base. Heavy industries are concentrated in Chiba, Kawasaki, and Yokohama, while Tokyo proper is strongly inclined toward light industry, including book printing and the production of electronic equipment.
More significantly, perhaps, Tokyo is Japan's management and finance center. Corporations with headquarters or branches or production sites in other parts of the country often have large offices in Tokyo, Marunouchi being the location of many of these. The close relationship between government and business in Japan makes a Tokyo location advantageous if not necessary.
To the north of Marunouchi is Otemachi, where Japan's leading financial institutions and insurance companies are located. Otemachi is also home to NTT, the communications giant. Of course, Tokyo is also the site of the Tokyo Stock Exchange, located in Kabutocho.
Tokyo was particularly affected by an economic boom in Japan in the 1980s when the country emerged as a global financial center rivaling Europe and the United States. The economic upswing led to speculation, and especially to real estate speculation. Land prices soared at the time, as did the value of the yen. The economy leveled out by the early 1990s, but Tokyo real estate remained the most expensive in Japan and held a similar rank on a global scale.
Why to Attend??? :
2nd International Conference and Exhibition on Nanomedicine and Drug Delivery - 2018 which will be the greatest gathering devoted to Nanomedicine and Drug delivery.
• Professionals giving a chief specialized gathering to detailing and finding out about the most recent new era advancements created over the span of time alongside examining their applications.
• Events incorporate intriguing issues introductions from everywhere throughout the world and expert systems administration with enterprises, driving working gatherings and boards.
• Meet Your Objective Business area with people from and around the world focused on getting some answers concerning Pharmaceutics and Nanotechnology , this is the most obvious opportunity to accomplish the greatest accumulation of individuals from wherever all through the World.
• Conduct appears, scatter information, meet with current, make a sprinkle with another item offering, and get name affirmation at this event. Generally acclaimed speakers, the most recent techniques, methodologies, and the most breakthrough updates in Pharmaceutics and Engineering are indications of this meeting.
Nanomedicine Market in Japan:
Nanomedicine is a promising sub-segment in medicine that took off in the 1980s with the first generation of developed nanopharmaceuticals. With the use of nanotechnology, drugs can be delivered in ways not experienced so far.U.S. is a strong actor in this field with many patents having commercialized several nanopharmaceuticals.
The global nanomedicine market was valued at US$50.1 billion in 2011 and is projected to grow to US$96.9 billion in 2016. The share of nanomedicine to the total global pharmaceutical market is estimated at 5.3 percent in 2011 indicating its niche character presently.
In Japan, for various reasons, the nanomedicine market size in terms of the total market is much smaller. A rough estimate shows that the share is between 1 to 2 percent corresponding to approximately US$1 to 2 billion. A limited number of approved Japanese nanodrugs together with a long time until approved foreign products entered the Japanese market have seemingly slowed the market expansion.
Japan = World's 2nd largest pharmaceutical market!
- Japan is the 2nd largest pharmaceutical market in the world, marking JPY 10 trillion (USD 84.4 billion) in ethical drug in 2016.
- Nikkei Stock Average has been continuously increasing since mid October, 2016.
- The government is to ease the regulations to develop new medicines for intractable diseases by shortening 5 years of drug development time.
- Japan hugely depends on imported pharmaceutical products. The annual import value in Japan was JPY 1.94 trillion (USD 16 billion) in 2015 compared to the export value of JPY 0.32 trillion (USD 2.7 billion).
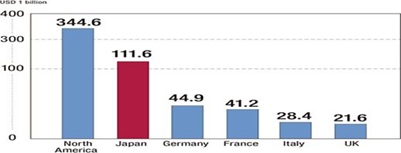
Japan’s pharmaceutical industry is the world’s second largest market, after U.S., valued at US$112.1 billion in 2012 or 11.6 percent of the world market. Historically, the market has been protected from foreign competition. These days, however, deregulation has prompted investment from abroad and increased the presence of foreign companies. The pharmaceutical industry is one of the few industrial sectors in which Japan has a trade deficit. Japan imports more than two times what it exports. The rapid aging of the population and the weak global competitiveness of domestic companies are contributing factors to the trade deficit.
Japan Nanomedicine Market Size:
There is no market information available on the size of Japan’s nanomedicine market published by any of the large Japanese market research companies. Table 2 below tries to estimate the market size. The global nanomedicine market was estimated to be about 5 percent of the global pharmaceutical market in 2010 and 2011. In case of Japan, this ratio is much lower compared to the global nanomedicine market. A rough estimate indicates that the market size was approximately 1-2 percent of the Japanese pharmaceutical market in 2011-2012, or roughly between US$1 billion – US$2 billion. The drug lag of imported nanopharmaceuticals is one cause of this. Nanomedicines have not been defined in Japan and are regulated within the general framework of the Pharmaceutical Affairs Law (PAL) on a product-by-product basis .
Approved Nanopharmaceutical Products by Application:
As there is no specific definition for drug and device (nanocarrier) combinations, they are regulated as drugs or medical devices according to their main function or purpose.
Pharmaceuticals are classified as nanomedicine by their sizes, i.e. materials in the submicron range.Information on marketed nanopharmaceuticals in Japan comes from various sources including “Current Initiatives in Japan for Nanomedicines”, Kumiko Sakai-Kato, Toru Kawanishi, 2011, National Institute of Health Sciences (NIHS) and Ministry of Health, Labour and Welfare (MHLW) .
- Unit: USD Billion Source: Japan Pharmaceutical Manufacturers Association “Data Book 2016”
|
Trade name |
Technology |
Compound |
Company |
|
Ropion |
Lipid emulsion |
Flurbiprofen |
Kaken (JPN) |
|
Visudyne |
Liposome |
Verteporfin |
Novartis |
|
Zevalin |
Antibody Conjugates |
Zevalin |
Bayer |
|
Somavert |
PEGylated protein |
Pegvisomant |
Pfizer |
|
Emend |
Nanocrystal |
Aprepitant |
Merck |
|
Abraxane |
Polymeric Nanoparticles |
Paclitaxel |
Abraxis |
Government Pushing for Change:
Order to reduce the time span from discovery and innovation to commercialization, the importance to establish open user facility networks to promote the integration of dissimilar fields and academic-industry collaboration is emphasized.
It is apparent that the government is aiming at more concrete and speedy results for R&D. Issue-driven innovation based on “exit-oriented” R&D is targeted to impact the competitive power of related industries.
A report by the Japan Science & Technology Agency titled “Japan’s New Science and Innovation Policy – Beyond the Boundaries for Innovation”, published in 2016 (50) lists up the time span for selected target applications of nanomedicine, such as:
- Molecular imaging (2015-2020)
- Integrated system of drug delivery, diagnosis and treatment (2015-2020)
- Implant devices for diagnosis and treatment (2020-2030)
- Nano-cell surgery (2020-2030)
- 3D-imaging in cells (2020-2030)
These are quite ambitious targets showing the directions where R&D will be focused.
In addition to the latest basic plan, there are other signals that the government is increasingly prioritizing innovative medicine. For instance, The Ministry of Health, Labour and Welfare will jointly with the European Union (EU) promote the development of nano-based block copolymer micelles. Together with European Medicines Agency (EMA) the ministry has released a reflection paper (February 2013) emphasizing that such micelles are able to preferentially accumulate in solid tumors (51).
Nanomedicine – Research and Development in Japan:
- University of Tokyo
- Hokkaido University
- Osaka Prefecture University
- Osaka University
- Tohoku University
- National Institute for Materials Science
The Japanese Nanomedicine Industry:
Nanomedicine start-ups and small-medium enterprises have driven the innovation process, not only in US and Europe but also in Japan. The commercialization of nanopharmaceuticals have basically followed three types of business models , such as:
- Development of a nanotechnology platform used to add value to second-party products
- Development and manufacturing of high-value materials for the pharmaceutical industry
- Development of nanotechnology-improved pharmaceuticals or medical devices
The majority of start-ups has adopted the third business model utilizing nanotechnology to develop own proprietary product pipelines. Often such companies introduce new or standard drugs that are delivered with a drug delivery system. Then they try to team up with pharmaceutical companies that take the products through the clinical trials.
- NanoCarrier Co., Ltd.
- LTT Bio-Pharma Co., Ltd.
- Mebiopharm Co., Ltd.
- Nippon Kayaku Co., Ltd
- Kowa Company Ltd.
- Mitsubishi Tanabe Pharma Corporation
- Taisho Pharmaceutical Co., Ltd.
- Astellas Pharma Inc
- Kaken Pharmaceutical Co., Ltd.
Drug Delivery Devices market in Japan:
Japan has one of the world’s most advanced healthcare facilities. The healthcare administration in Japan is also becoming a model for many developing nations.
The report details several factors driving the market, some of which are listed below.
Drivers
· Increased prevalence of chronic diseases
· Advances in drug delivery system
· Increase in individual therapy
· Increased understanding about drug metabolism among the population
· Increasing demand for generic drugs
· Requirement of controlled drug release
Japan’s drug delivery market has been segmented into oral drug delivery systems, nasal drug delivery system, pulmonary drug delivery system, injectable drug delivery, ocular drug delivery, topical drug delivery, transmucosal drug delivery and implantable drug delivery. The segmentation on oral drug delivery system is sub-divided into solid oral drugs (includes tablets, capsules, powders, and pills), liquid oral drugs (includes syrups and solutions), semi-solid oral drugs (includes gels, emulsions, suspensions, and elixirs). The segmentation on nasal drug delivery systems has been subdivided into nasal drops, nasal sprays, nasal powders, nasal gels. The segmentation on pulmonary drug delivery systems includes metered dose inhalers, dry powder inhalers, and nebulizers. The segmentation on injectable drug delivery has been further segmented into general injectable, self -injection device, needle-free injectors, auto-injectors, and pen injectors.
The global drug delivery system market size was valued at USD 379.2 Billion in 2015. Growing efforts towards formulating dosage forms that would help in maximizing the bioavailability of the drug at the target site while increasing the patient convenience are driving the global market growth. The introduction of the novel drug delivery systems such as subdermal implants that are available in different forms such as rings and patches are expected to aid in the industry growth.
The evolution of the drug delivery systems is directly attributed to changing preferences by patients as well as healthcare professionals. A few of the many advancements include-
• Introduction of Biopharmaceutical classification systems (BCS) class II drug in oral dosage forms
• Introduction of auto-injectors
• Availability of advanced implants in customized shapes and sizes
• Introduction of advanced pulmonary devices such as Smartcard and Adaptive Aerosol Delivery
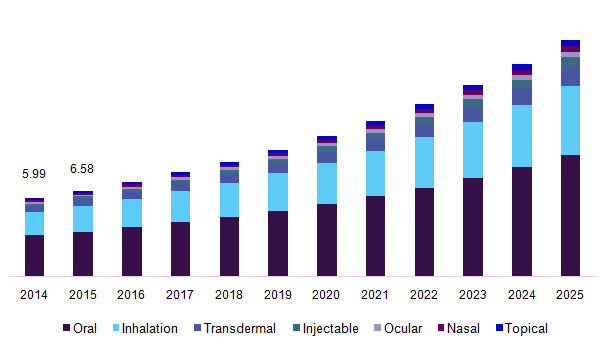
Japan drug delivery systems market, by route of administration, 2014 - 2025 (USD Billion)
Global Tissue Engineering Market:
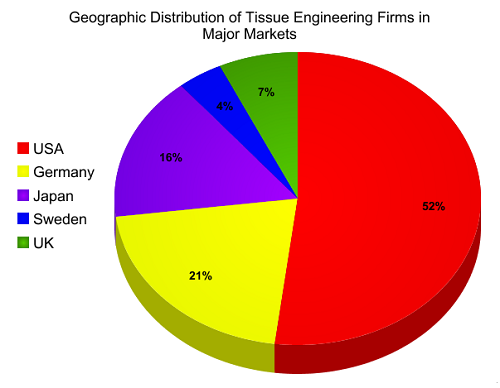
The global tissue engineering and cell therapy market stood at nearly $9.9 billion in 2014 and is forecast to see an annual average growth rate of 21% to reach a value of around $73 billion by 2025.
Tissue Engineering is a process involving in-vitro development of tissues or organs. It is done to replace or support the function of defective or injured body part. Tissue engineering involves the application of biology and engineering for innovation of tissue substitutes that can maintain, restore and improve the function of ruptured human tissue. Products developed by this procedure are efficient and durable. Tissue engineering is gaining its popularity in various areas such as burn treatment or wound care, neurology products, orthopedics, urological products and others. On the basis of type of material used, tissue engineering and regeneration market can be segmented into synthetic, genetically modified and biological materials.
The global regenerative medicines market is anticipated to achieve USD 50.11 billion by 2021, registering a CAGR of 12.7% during the period of 2015-2021. On the back of expanding demand for bone and joint reconstructive surgeries within the nation, North America with the most shares in global regenerative dominated the market followed by Europe in 2015. Further, it's projected that by 2019 Europe might surpass the North America market in the field of stem cell and regenerative medicine. Eastern and Western Europe are anticipated to demonstrate extended request in light of the fact that the requirement for transplants through regenerative drugs will be expanding for several applications in coming future. Asia-Pacific countries are required to show up-surged request amid 2015-2021. In addition to that, Asia-Pacific transforming into one of the prime mainlands in providing regenerative medicines on bone and joint in nations like India, China, Japan and South Korea are anticipated to give a lift to the stem cell market within these countries .
- Pharmaceutical Regulations in Japan:
- Manufacturing, importation, and sales of drugs and medical devices are regulated by the Pharmaceutical Affairs Law (PAL) of Japan.
- All manufacturing and marketing applications in Japan for drugs and devices are reviewed by the Pharmaceutical and Medical Devices Agency (PMDA) . All applications are thoroughly reviewed before PMDA submits an approval recommendation to the Ministry of Health, Labour and Welfare (MHLW).
- Under PAL, when importing to Japan and selling pharmaceutical products manufactured in other countries, a license for marketing authorization is required. The Marketing Authorization Holder (MAH) will be the owner of the license for marketing authorization.
- The MAH must be based in Japan and can be the foreign company’s Japan office, the foreign company’s distributor, or an independent third party acting as the Designated Marketing Authorization Holder (DMAH).
- To import and market a new drug in Japan, an approval (marketing approval) will be necessary. And the approval must be held by the Marketing Authorization Holder.
- A foreign manufacturer intending to manufacture drugs in foreign countries and export them to Japan, is required to be accredited by MHLW as an “Accredited Foreign Manufacturer” (84). And it is necessary to obtain accreditation for each foreign factory location at which pharmaceuticals for export are manufactured.
- The appointed MAH will be responsible for the labelling and advertising of the pharmaceuticals in Japan. As stipulated in PAL, the manufacturer’s/seller’s address, name of product, production indication, name of ingredients, expiration, etc., must be printed on the container of drugs.
- Overall research in various disciplines:
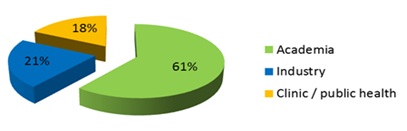
The North American nanomedicine market held the majority of global market share in 2012 because of the rapidly growing nanomedicine market in the Asia-Pacific, Latin American and African region, presence of large number of patented nanomedicine products and favorable regulatory framework in the region. In addition, the presence of sophisticated healthcare infrastructure supports development of advanced products such as nano probes, nanorobots, monoclonal antibody based immunoassays and nanoparticle based imaging agents for early detection of diseases.
However, the Asia-Pacific region is expected to grow at a faster CAGR owing to presence of high unmet healthcare needs, research collaborations and increase in nanomedicine research funding in emerging economies such as China, India and other economies in the region. China is expected to surpass the United States in terms of nanotechnology funding in the near future, which indicates the growth offered by this region.
Major Nano Delivery Associations around the Globe:
- American Nano Society
- European Biotechnology Thematic Network Association
- Society for Biomaterials
- Nano Canadian Society
- American Academy of NanoMedicine
- American Association for the Advancement of Science
- Nanometer-Scale Science and Technology Division of the American Vaccum Society
- NanoScience and Technology Institute
- ASME NanoTechnology Institute
- Foresight Nanotech Institute
- International Association of NanoTechnology
- The Institute of NanoTechnology
- Microscopy Society of America
- Nano Business Alliance
- European NanoTechnology Gateway
- Scottish Center for NanoTechnology in Construction Materials
- Royal Society-NanoTechnology and NanoScience
- Czech NanoTechnology Industries Association
- Erwin Schrodinger Society for NanoSciences
- Innovationsallianz Carbon NanoTubes
- NanoTechnologies for Tommorow's Society
- American Association for the Advancement of Science
Companies involved in Nano Delivery:
USA
- Oncolytics Biotech
- Bristol-Myers Squibb
- GlaxoSmithKline
- Bend Research
- Pfizer
- BioDelivery Sciences
- GE Healthcare
- Mallinckrodt plc
- Nanosphere Inc., USA
- Pfizer Inc., USA
- Merck & Co Inc., USA
- Celgene Corporation, USA
- CombiMatrix Corporation, USA
- Abbott Laboratories
- Many Major companies in the Nano Delivery market.
Global

Conference Highlights
- Advanced Nanomedicine
- Design of Nanodrugs
- Personalized Nanomedicine
- Recent Nanomaterials for drug delivery
- Emerging technologies on Nanomedicine and Nanotechnology
- Synthesis of Nanoparticles for Drug Delivery
- Drug Delivery Research
- Novel Drug Delivery Systems
- Smart Drug Delivery Technology
- Regenerative Medicine and Tissue Engineering
- Nano Pharmaceuticals
- Major challenges in Nano Pharmaceutical Industry and Market
- Regulatory Aspects Towards Approval of Nanomedicine
- Biopharmaceutics and Biologic Drugs
- Nanomedicine in Theranostics
- Graphene Medicine
To share your views and research, please click here to register for the Conference.
To Collaborate Scientific Professionals around the World
| Conference Date | May 21-23, 2018 | ||
| Sponsors & Exhibitors |
|
||
| Speaker Opportunity Closed | Day 1 | Day 2 | Day 3 |
| Poster Opportunity Closed | Click Here to View | ||
Useful Links
Special Issues
All accepted abstracts will be published in respective Our International Journals.
- Journal of Nanomedicine & Nanotechnology
- Journal of Pharmaceutics & Drug Delivery Research
- Journal of Pharmaceutical Sciences & Emerging Drugs
Abstracts will be provided with Digital Object Identifier by



















































